16 People Who Witnessed Odd Things Too Wild Not to Tell


We all know the feeling of rushing through a meal — whether it’s grabbing lunch between meetings or finishing dinner in record time. But eating too fast can do more than just leave you with an uncomfortably full stomach. From digestive issues to long-term health risks, this habit can quietly take a toll on your body and even affect your appearance.
CONTENT IS PROVIDED FOR INFORMATIONAL PURPOSES ONLY AND IS NOT INTENDED AS A SUBSTITUTE OF MEDICAL ADVICE. SEEK GUIDANCE OF YOUR DOCTOR REGARDING YOUR HEALTH AND MEDICAL CONDITIONS.
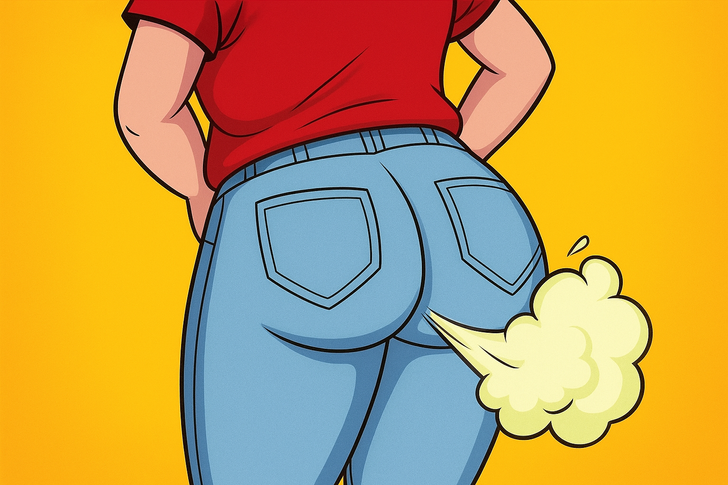

Eating too quickly causes you to swallow more air along with your food, which increases the buildup of gas in your digestive tract. This can lead to uncomfortable flatulence. The types of foods often eaten in a hurry — such as carbonated drinks, fried snacks, or high-fat meals — can worsen the problem. Taking smaller bites, chewing thoroughly, and eating at a calmer pace can help reduce excess gas and ease digestive discomfort.
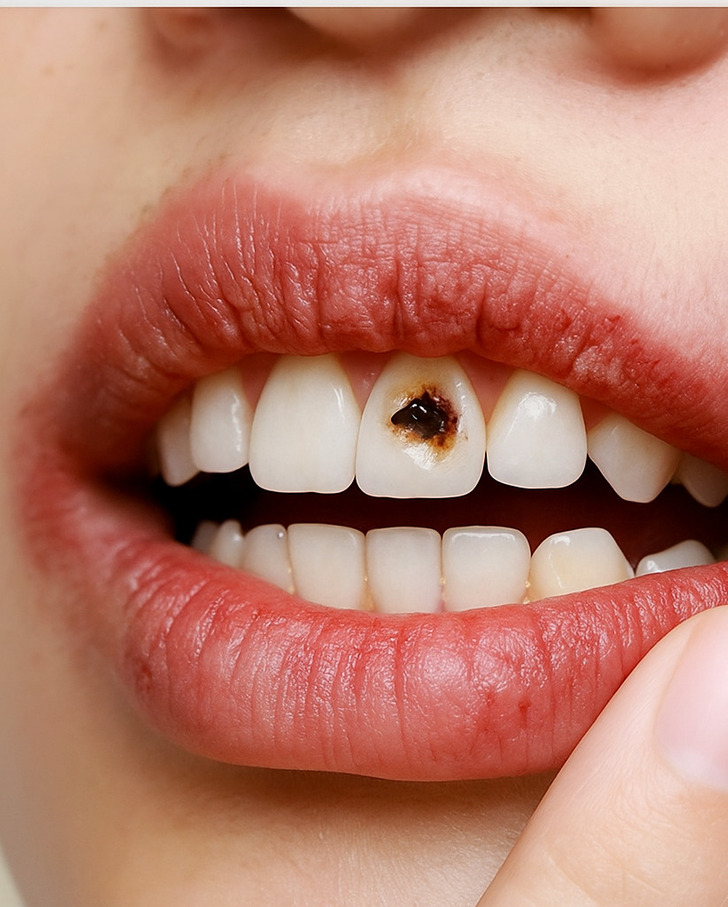

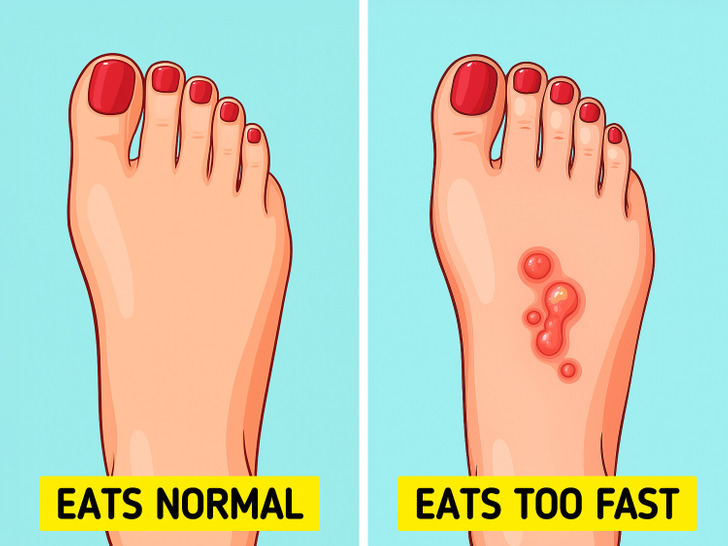
Fast eating doesn’t directly cause cavities, but it can raise the risk. Chewing less means bigger food particles stay stuck between teeth, giving bacteria more to feed on. It also reduces saliva flow — the natural defense that washes away acids and protects enamel.
Between meals, there’s usually a period where saliva can work to neutralize acids and wash away sugars. If you’re constantly eating or finishing meals too quickly and then snacking etc., you give less “break time” for your mouth. Over time, this can lead to more plaque, more acid attacks, and eventually tooth decay.
Common Symptoms of Type 2 Diabetes:

Fast eating is linked to poor digestion, which can trigger inflammation in the body. In some people, this shows up on the skin as acne, dullness, or uneven texture. Nutrient absorption may also suffer, leaving your skin looking less vibrant because it isn’t getting enough vitamins and antioxidants.
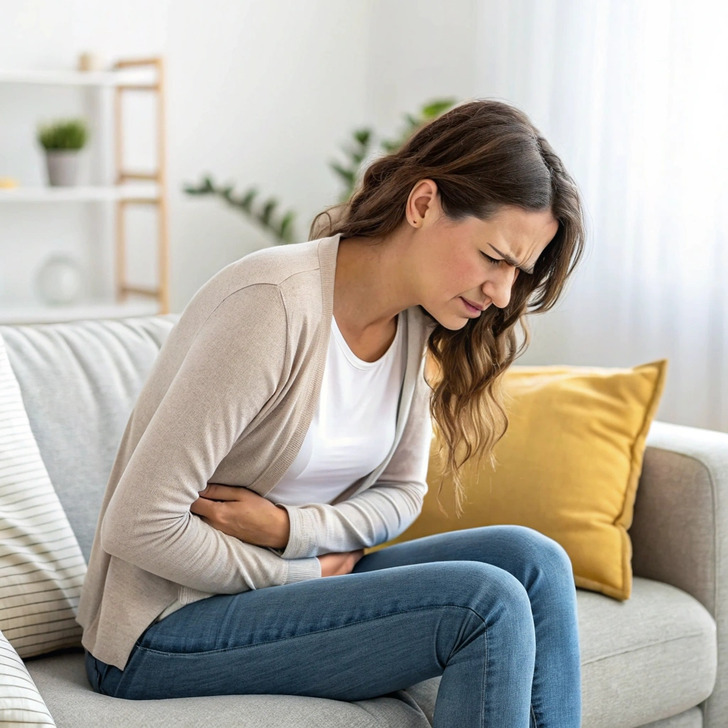

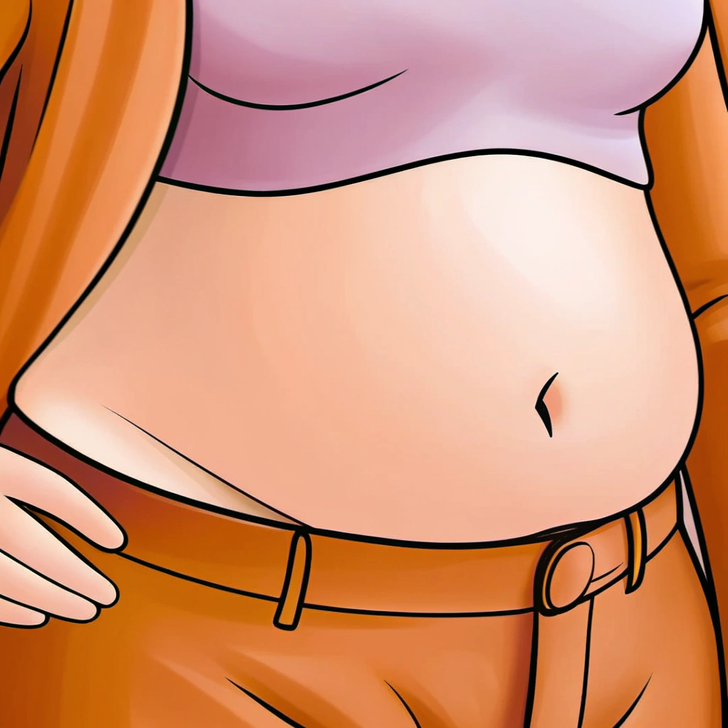
Eating too quickly often means swallowing more air, which leads not only to increased flatulence but also to bloating. This doesn’t just make your stomach feel uncomfortable — it can also make your midsection look swollen. Slowing down helps reduce trapped air and gives a leaner, more relaxed appearance.











