Donatella Versace Debuts with a “NEW FACE” — She Looks Unrecognizable!

Sleep apnea doesn’t just disrupt your sleep - it can have serious consequences for your overall health. While some risk factors, like age and genetics, are unavoidable, others can be managed with lifestyle changes and medical intervention. Understanding what increases your risk can help you take proactive steps toward better sleep and well-being.
CONTENT IS PROVIDED FOR INFORMATIONAL PURPOSES ONLY AND IS NOT INTENDED AS A SUBSTITUTE OF MEDICAL ADVICE. SEEK GUIDANCE OF YOUR DOCTOR REGARDING YOUR HEALTH AND MEDICAL CONDITIONS.
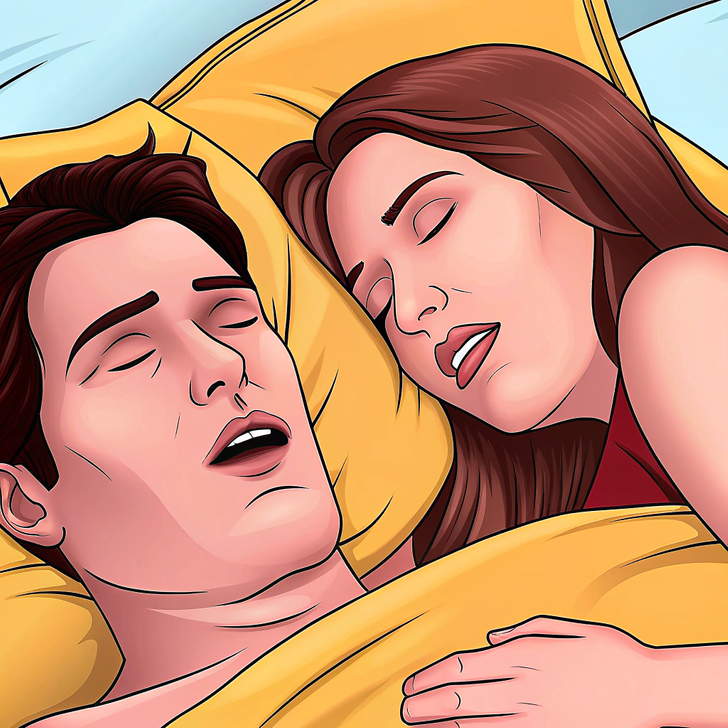

Sleep apnea is a serious disorder marked by repeated breathing interruptions during sleep. Common symptoms include loud snoring and daytime fatigue, even after a full night's rest. Untreated sleep apnea can affect daily functioning and lead to severe health risks, including diabetes and heart issues.
Statistics indicate that up to 30 million Americans may have sleep apnea, often without diagnosis. Being aware of its symptoms helps determine when to see a doctor.
There are three types of sleep apnea:
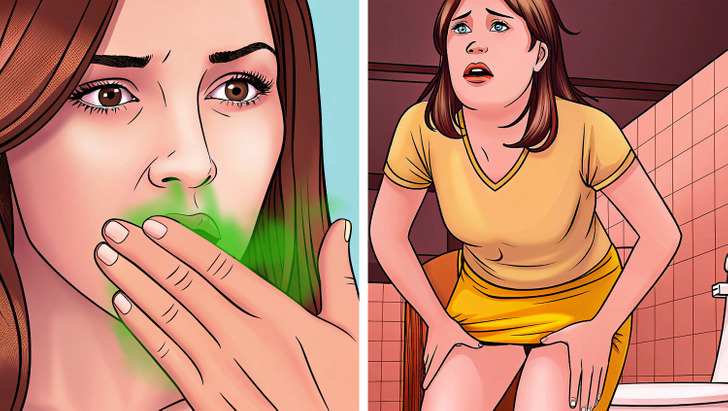

Here are the symptoms of sleep apnea, both common and uncommon.
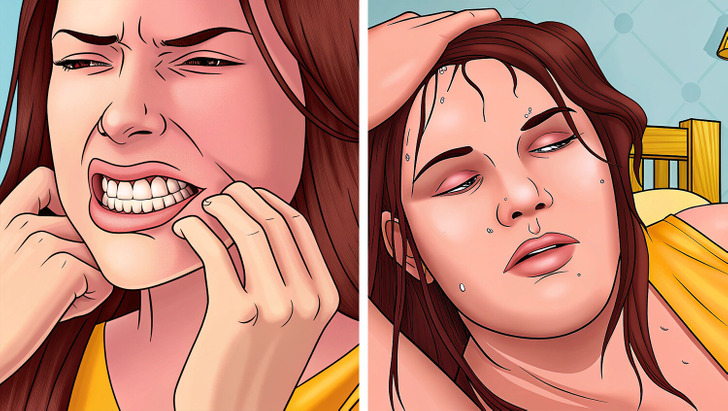

If you or a loved one experience these symptoms, consider consulting a healthcare professional for evaluation.

Obstructive sleep apnea can stem from various conditions, with some risk factors being changeable and others not. According to the National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute, key factors include:


Sleep apnea can range from mild to severe, assessed using the apnea-hypopnea index (AHI), which measures breathing pauses during sleep.
Severe: AHI > 30 (over 30 episodes per hour)
Moderate: AHI 15-30
Mild: AHI 5-15
Addressing sleep apnea is crucial to prevent long-term health effects.

Making specific lifestyle adjustments can help mitigate the risks of sleep apnea:
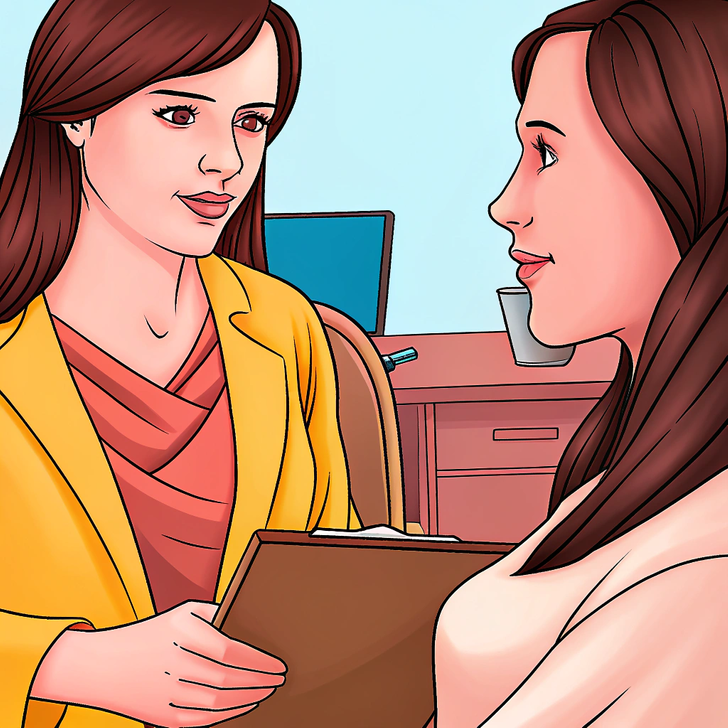

If you or your partner observe symptoms of sleep apnea, consult a healthcare provider. They may review your health history, recommend a sleep study, and discuss lifestyle changes or CPAP treatment.
Regular follow-ups are essential to evaluate treatment effectiveness and address any new sleep issues.











