18 Stars Who Left Us in Awe With Their Major Makeover


The human body is like a puzzle full of surprises. All these tiny parts inside us work together, reacting in a domino effect due to things around us or the decisions we make. People have been studying it for thousands of years. And yet, there are still lots of things we’re finding out about it! Let’s dive into eight mind-blowing facts that you’ve probably never heard before. Get ready to be amazed!

Although rare, male lactation is known to occur under specific circumstances. This phenomenon is caused by the hormone prolactin, which can cause anyone who is not pregnant or breastfeeding to produce milk. While it is generally thought to be biologically impossible for men to lactate, some anthropological research suggests that it can happen.
For instance, in her book Tender Gift: Breastfeeding, medical anthropologist Dana Raphael wrote that men can induce lactation through nipple stimulation. However, for milk production to take place, a hormone surge must occur, which is unlikely in most male bodies.
Scientists believe that throughout human evolution, we’ve acquired around 100,000 bits of DNA from retroviruses. Animals like chimpanzees, gorillas, and orangutans are quite similar to us, sharing about 96% of our genes. Surprisingly, we’re also genetically connected to bananas and slugs. We carry 50% of the genetic code of bananas and 70% of slugs.
Here’s an interesting fact: nearly 99.9% of our genetic makeup is the same in every person. It’s that tiny 0.1% difference that gives us diverse skin, hair, and eye colors. Moreover, researchers think this remaining 0.1% contains vital information about how diseases begin.
Your brain begins to shrink as you enter your 30s or 40s, and this shrinkage accelerates when you reach 60. Not all aspects of your memory decline at the same pace — certain parts fade faster than others. Some areas experience a rapid decrease, surpassing their neighboring regions, and this tendency tends to worsen with age.
While aging is a natural process, you can support your brain’s well-being by staying physically active, maintaining a balanced diet, and addressing any worries you have with your doctor.
Belly button lint originates from the hair on your stomach, according to scientist Sejal Shah. This navel debris is a mix of dead skin cells, fibers from clothing, sweat and oil traces, and assorted particles. Because men tend to have more stomach hair, they often accumulate extra lint in their belly buttons. Soren White, a certified dermatologist in New York City, explains that individuals with inner belly fat, where fibers can get trapped, typically only need to be concerned about fluff in the lower abdomen.
Sejal Shah suggests that those with thicker and longer body hair are more prone to finding impurities on their stomachs. Women are less susceptible because their stomach hair is generally finer and shorter compared to men’s. Nevertheless, both White and Shah conclude that regular belly button cleaning significantly reduces the likelihood of this issue.
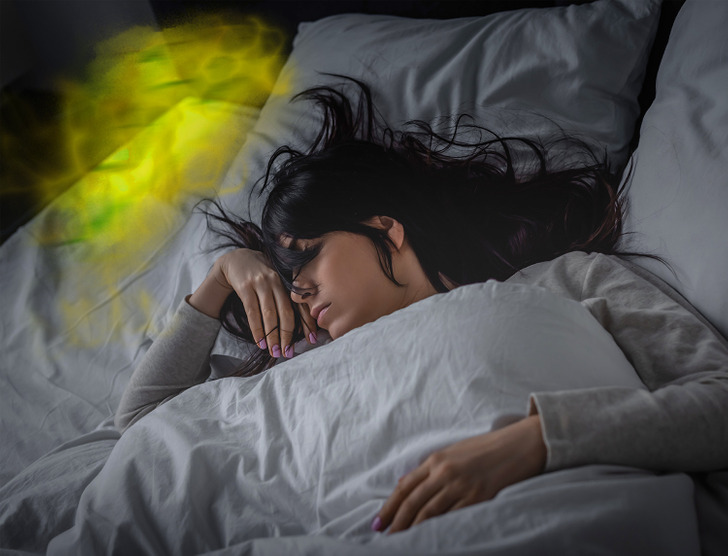

At Brown University, Rachel Herz, a professor of psychiatry, has spearheaded research endeavors aimed at unraveling the mysteries of the REM (rapid eye movement) phase of sleep, renowned as the dream period. Through her investigations, she has uncovered a peculiar phenomenon: during the REM state, individuals lose their ability to perceive odors. As she elucidates, “The scent of coffee won’t rouse you. Its flavor, however, might.”
Herz arrives at the conclusion that in the realm of hallucinations, the absence of olfactory senses prevents us from engaging with the real world. Nonetheless, she underscores that a partial awakening from a dream, followed by a sniff of a pleasant aroma, might lead to full consciousness, akin to being roused by the delightful fragrance of coffee. In her perspective, the scents woven into our imaginings are a construct of the mind, originating internally rather than from the external environment.
Tattoo ink is inserted into tiny pores beneath the skin’s surface, effectively preserving the image for the long haul. Your body’s response to fresh ink involves two distinct reactions, both stemming from your natural anatomy’s defense mechanisms. When you get a new tattoo, your immune system reacts by deploying white blood cells to devour the foreign substances, acting as both defenders and sacrificial guardians to ward off potential infections.
Immunologists refer to our body’s reaction to tattoos as “adaptive.” Specific blood proteins are programmed to confront unwelcome invaders, lingering within the bloodstream to stand guard against any future assaults from the same source. This proactive readiness ensures swift and efficient responses when needed.
Though we often view our memories as a meticulously detailed camera, capturing each moment with unwavering accuracy, the disappointing truth is that they resemble more of a patchwork. We assemble fragments haphazardly, sometimes with added embellishments or outright falsehoods.
Our perception isn’t always the most reliable. Occasionally, we perceive objects that lack existence while overlooking glaringly obvious details right before us. Many misunderstandings arise because the initial information wasn’t correctly encoded.
For instance, consider witnessing an event without a full grasp of all its facets. In such cases, recalling what transpired can prove challenging or even unattainable due to incomplete observation. To bridge these “gaps,” our minds might conjure impressions that never truly unfolded.
Your left lung is divided into two lobes, whereas the right side is divided into three. The left lung is slightly smaller to accommodate your heart. In the world of human lungs, over 300 million tiny air sacs, known as alveoli, coexist, alongside a sprawling network of airways stretching more than 1,500 miles in total length.
The eye possesses remarkable swiftness in its movement across all directions, rendering it the fastest among bodily components. It outpaces other muscles, even orchestrating their motions — like raising hands in rapid defense against an impending threat. This influence originates from the intricate dance of extraocular nerves governing eye movement, showcasing their preeminence among ocular reflexes.
Intraocular contractions orchestrate the iris’s opening and closing, allowing light to flood the pupil and facilitating other vital functions. Nonetheless, these responses fall short in velocity compared to the agility of the oculomotor system. Vital to ocular vitality, regular blinking nurtures and oxygenates the eyes while clearing away dust and debris. On average, the eyes engage in this rejuvenating rhythm at a rate of 15 to 20 times per minute.
Just when you thought the realm of bodily oddities couldn’t get any more intriguing, a whole new dimension of fascination awaits. Prepare to transition from the peculiar to the exquisite, as we venture into the alluring world of celebrity bodies, dissecting the science behind their undeniable allure.











