8 Red Flags Clearly Indicating an Unhealthy Relationship
Protein is a vital nutrient that supports muscle strength, skin health, and the production of essential enzymes and hormones. However, many people don’t get enough of it, which can lead to various health issues. A lack of protein can affect your metabolism, energy levels, and even your weight. If your body isn’t getting enough, it may start showing warning signs. Below, we’ve gathered some key indicators of protein deficiency to help you recognize if you need to boost your intake.
CONTENT IS PROVIDED FOR INFORMATIONAL PURPOSES ONLY AND IS NOT INTENDED AS A SUBSTITUTE OF MEDICAL ADVICE. SEEK GUIDANCE OF YOUR DOCTOR REGARDING YOUR HEALTH AND MEDICAL CONDITIONS.

One of the most typical signs of not getting enough protein is swelling — also called edema. The swelling usually happens in your abdomen, legs, feet, and hands. A possible reason for this symptom is to have low levels of a substance called albumin.
Albumin helps keep fluid inside the blood vessels. A lack of albumin can make it hard for the body to balance fluid in blood vessels, which results in fluid accumulation in the body tissues. The body tries to hold onto more water and sodium, which causes swelling. It’s good to bear in mind that edema is a symptom of severe protein deficiency, which is unlikely to occur in developed countries.

Protein deficiency weakens the immune system by impairing the body’s ability to produce antibodies and cytokines. Cytokines are also involved in wound repair, so protein deficiency is associated with slowed wound healing. People who are low on protein often find their cuts and scrapes take longer to get better. The same seems to be true of sprains and other exercise-related mishaps.
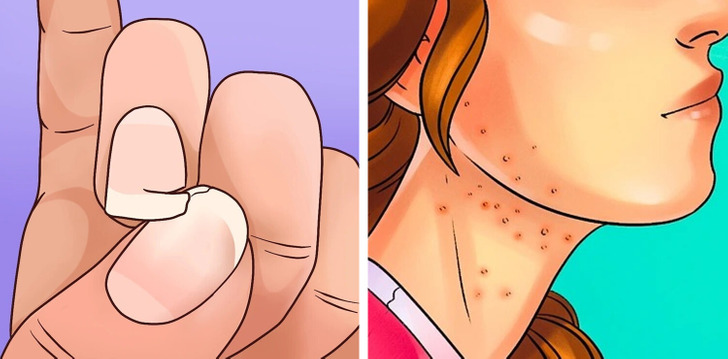
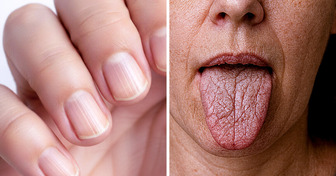
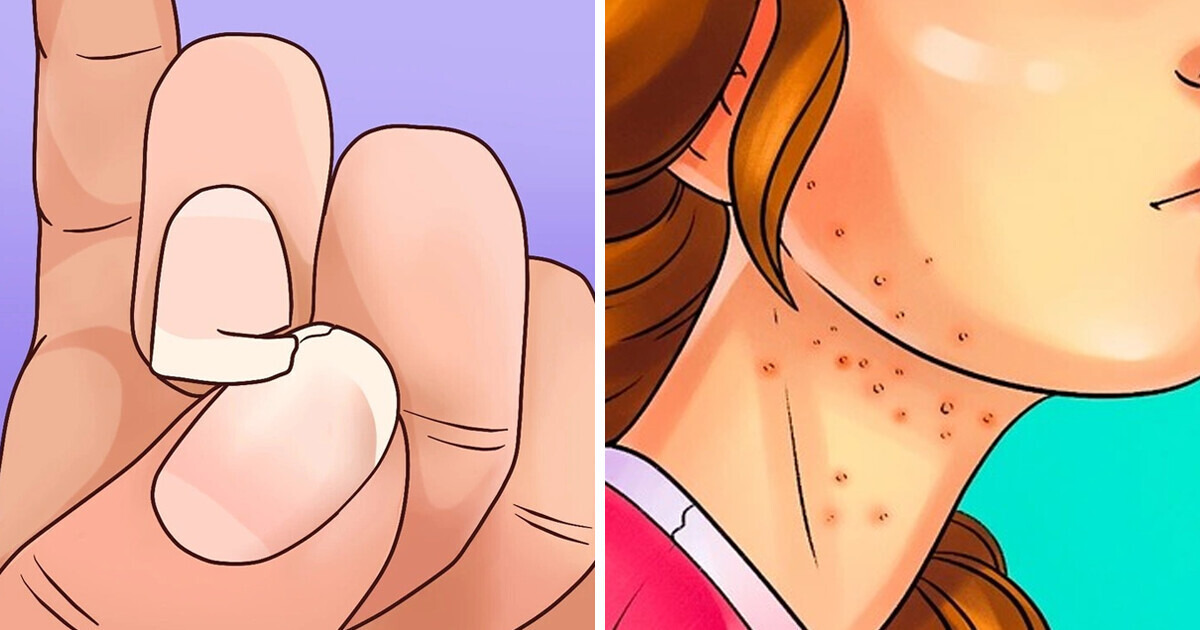
Protein is a major component of skin and hair. When your body can’t make them, protein deficiency can cause your skin to appear paler, drier, or flakier. Your hair may appear more brittle, while your fingernails can have deep ridges.
Protein provides the amino acids crucial for the production of neurotransmitters which relay information between cells. So a lack of protein in your diet could mean your body can’t make enough of those neurotransmitters, and it might change how your brain works. With low levels of dopamine and serotonin, for example, you may feel depressed or overly aggressive.

Not eating enough protein can make you lose muscle mass, which will cut your strength, make it harder to keep your balance, and slow your metabolism. It can also lead to anemia when your cells don’t get enough oxygen, which makes you tired.
A severe protein deficiency can impair your immune system. Protein helps make antibodies that protect you from infection and other illnesses. Protein deficiency leads to fewer antibodies, which can increase your risk of infections. There’s also evidence that protein can change the levels of disease-fighting “good” bacteria in your gut.

A protein deficiency can affect your weight. Without enough protein, your body may lose muscle instead of fat, slowing down your metabolism and making it harder to burn calories. At the same time, low protein levels can increase cravings and make you feel hungrier, leading to overeating and potential weight gain.
Here, you can learn about the symptoms of deficiencies in protein and other micronutrients.